You caught a beauty!!!
Download the PDF of the scaffold here.
theory behind scaffold…
Cultural differences extend far beyond language, greetings, gestures, dress and beliefs. The very space we create when we meet people – or the absence of that space – is indicative of where we come from and what our understanding is of the (dis)comfort level of those we are with.
This scaffold helps us see how we can honour physical space, amongst many other differences between cultures. It includes ……………………………………..
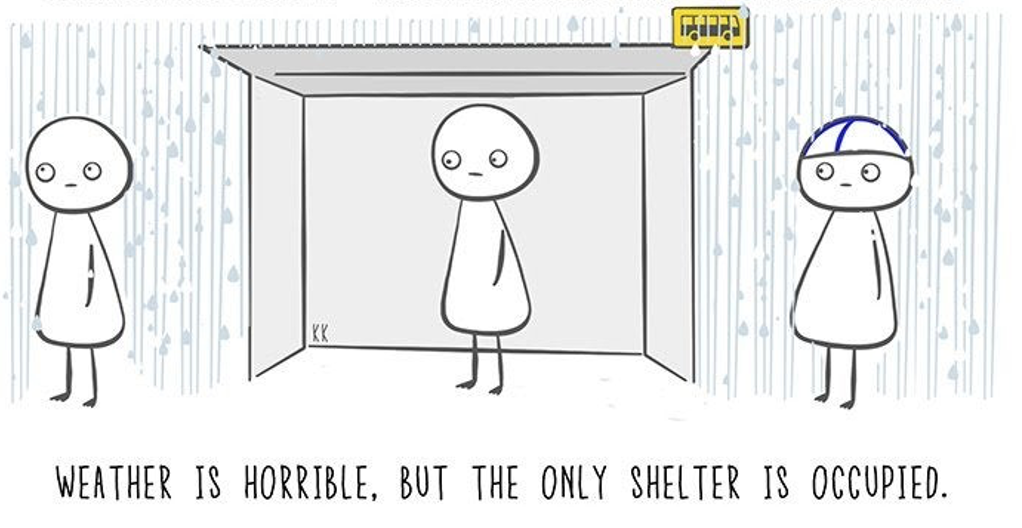
The image to the right is an amusing look at Finnish cultural peculiarities, drawn by a Finnish artist Karolina Korhonen, in her hugely popular Finnish Nightmares. It shows …………………………………. empathise with other’s comfort levels.
Emotional intelligence is defined as ‘the capacity for recognising our own feelings and those of others, for motivating ourselves, and for managing emotions well in ourselves and in our relationships.’ (Goleman 1993:317). Findings show that emotional intelligence is ………………………………………
Step by Step…
- Elicit affective responses by getting students in groups, standing and facing each other and taking turns slowly taking three steps towards each of their classmates and then three steps back. They n……………………………………………………..and how their classmates say they felt.
- Begin a more focused conversation through the following material:
- studying Hall’s four (4) zones of personal space: public, social, personal, intimate (family) and debate ……………………..
- watch the first 30 seconds of the video Invading Personal Space with ………………………………………………. and what they would do it this happened.
- give students a copy of the comic strip ‘Finnish Nightmares: Public Spaces (Bus Stop).
- read some striking differences between …………………………….
- study the scenes in the cartoon frames below.
- Based on the information chosen, students formulate two (2) lower-order thinking questions and three (3) higher-order thinking questions.

- When the woman moved close to the girl on the street, …………………………..?
- How do you think the girl was feeling when t…………………………….?
- What is the difference between how eye contact is perceived in Asia and Arabic countries?
- What if you decided not to smile at anyone for a year? How ……………………………….
- Students choose one cultural difference that they have learned and make it visible ……………………….

Scaffoldingmagic.com is your entryway into DYNAMIC bilingual learning methodologies, such as Phenomenon-Based Learning, CLIL, EMI, and ESL. You’ll find ways to implement critical thinking tools (DOK) to promote higher level thinking, the growth mindset, instill an ethic of excellence, deep reflection on learning, and all through multi-cultural, interdisciplinary activities. We have the keys to turning competences into action and to creating collective efficacy in your school so you move ahead as a unified, enthusiastic team.







Pingback: Robin Berlinsky: After-School programs and Partnerships that Promote 21st Century Skills - Scaffolding Magic